1、七种常见的数组排序算法整理(C语言版本)
Hot100
两数之和, ✔️
反转链表, 回文链表(1.快慢p拆,2.翻转 3. 判断), 相交链表 (f1: set() f2: A+B和B+A f3:快慢p) ✔️
最大子序和 (动态规划/分治法), ✔️爬楼梯, 打家劫舍 & 环形链表 , 合并2个有序链表, ✔️
有效的括号, 最小栈 ✔️
买卖股票的最佳时机-3, 两阶段 , ✔️买卖股票的最佳时机-4, 超难 翻转二叉树 , 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 , ✔️
只出现一次的数字, 汉明距离 x&(x-1)来统计二进制数x中1的个数 ✔️
二叉树的直径 & 二叉树的最大深度 & 对称二叉树, 合并二叉树 , ✔️
求众数 ,移动零 ,找到所有数组中消失的数字
最短无序连续子数组,找到字符串中所有字母异位词 , 路径总和 III
Page1
两数之和(方法:一遍哈希表) Map < Integer, Integer > , ✔️
最长回文子串
反转链表 , ✔️
LRU缓存机制
编辑距离
无重复字符的最长子串
戳气球
接雨水
两数相加 (链表+进位carry), ✔️
寻找两个有序数组的中位数
三数之和 (2方法: hash & 对撞指针) , ✔️最大子序和 (动态规划/分治法), ✔️字符串解码
删除无效的括号 最大矩形 有难度 nok全排列 (交换法,类比字符串思路) , ✔️合并两个有序链表 , ✔️
正则表达式匹配
零钱兑换 , ✔️
Page3
单词搜索 (DFS vector < vector < bool > > visit(row, vector < bool > (col, false)) )打家劫舍之三 (DFS)最小路径和
电话号码的字母组合
每日温度
回文子串
验证二叉搜索树
单词拆分
颜色分类
在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
字母异位词分组
完全平方数
环形链表 II
除法求值
课程表
根据身高重建队列
除自身以外数组的乘积
目标和
比特位计数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Solution public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> m = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); int [] res = new int [2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) { if (m.containsKey(target - nums[i])) { res[0 ] = i; res[1 ] = m.get(target - nums[i]); break ; } m.put(nums[i], i); } return res; } }
爬楼梯
1.1 easy
二维数组中的查找 bool Find(int b[][4], int rows, int cols, int value), ✔️替换空格 char* replace(char* str, int len) ‘ ’->%20 在源数组总长度,从后向前,逐个赋值, ✔️
数字在排序数组中出现的次数 biSea(arr,k+0.5)-biSea(arr,k-0.5); / bina(*a, len, num, isLeft), ✔️
旋转数组的最小元素 while(low < high) { if(a[m] > a[high]) min[m+1,high], else [low,m]} ✔️
调整数组位数使奇数位于前面 void odds(int[] arr) , ✔️
次数超过一半的次数 * int core(int *a, int len), ✔️
丑数 , 只包含质因子2、3和5的数称作丑数, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, … , ✔️和为S的两个数字(双指针思想) , ✔️
扑克牌顺子 (排序后,统计大小王数量 + 间隔), ✔️
构建乘积数组 (A数组,从前向后,再从后向前j-2,构造 B), ✔️
求1+2+3+…+n (判断 && 递归), ✔️
1.2 medium
八皇后和S连续正数序 (3fun,mid = (1+sum)/2; while(start<mid), Sum(int start, int end), 双vector), ✔️约瑟夫环 LinkedList; (index = (index + m) %link.size();link.remove(index--)😉 link.get(0); , ✔️
数组排成最小的数 Arrays.sort(str, new Comparator(){ public int compare(String s1, String s2),✔️ 数组中只出现一次的数字 , 划分2数组,num & (-num);二者与后得到的数,将num最右边的1保留下来,✔️
1.3 important
数组中的逆序对(归并排序). void mergeSort(int a[], int l, int r) , ✔️
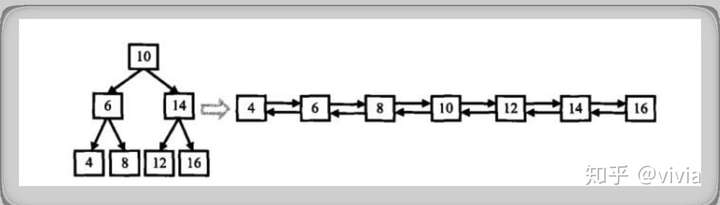
最小的K个数(堆排序), 数据流中的中位数 (2 PriorityQueue) .
最小的K个数 (2fun)快排思想 part return l, 外else return left; void set_k(int* input, n, k) , ✔️quickSort (a[],left,right), while(1) { (双while, if(l >= r) break; swap) } swap(a[left], a[l]);, ✔️最短路Floyd , ✔️
quickSort (1 while + [2while + break + swap] + swap + 2 quickSort)
mergeSort (2 mergeSort + new *arr + 3 while + 1 for)
1.1 八皇后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 const int N = 105 ;int pos[N];int num = 8 , cnt = 0 ;bool ok (int n) for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (pos[i] == pos[n]) return false ; if (abs (pos[n] - pos[i]) == n-i) return false ; } return true ; } void dfs (int n) if (n == num) { cnt++; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { pos[n] = i; if (ok (n)) { dfs (n+1 ); } } } int main () res = dfs (0 ); cout << res << endl; return 0 ; }
1.2 二维数组中的查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 int a[][4 ] = { { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }, { 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 }, { 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 }, { 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 }, { 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 } }; bool Find (int b[][4 ], int rows, int cols, int value) int row = 0 , col = cols - 1 ; while (b != NULL && row < rows && col >= 0 ) { if (b[row][col] == value) { cout << "row: " << row << " col: " << col << end; return true ; } else if (b[row][col] > value) { col--; } else { row++; } } return false ; }
1.3 替换空格
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 char * replace (char * str, int len) while (str[len] != '\0' ){ if (str[len] == ' ' ){ konglen++; } len++; } return '\0' ; }
1.4 旋转数组的最小元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void quickSort (int a[], int left, int right) if (left < right) { int l = left, r = right, x = a[l]; while (1 ) { while (l < r && a[r] >= x) r--; while (l < r && a[l] <= x) l++; if (l >= r) break ; swap (a[r], a[l]); } swap (a[left], a[l]); quickSort (a, left, l-1 ); quickSort (a, l+1 , right); } }
1.5 调整数组位数使奇数位于前面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void reorderOddEven (int [] arr, len) if (arr == NULL || len <= 1 ) { return ; } int l = 0 , r = len - 1 ; while (l < r) { while (l < r && arr[r] % 2 == 0 ) { r--; } while (l < r && arr[l] % 2 == 1 ) { l++; } if (l < r) { swap (arr[l], arr[r]); l++, r--; } } }
1.6 出现次数超过一半的次数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 int core (int *a, int len) if (arr == NULL || len <= 0 ) { return ; } int target = a[0 ], cnt = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++) { if (a[i] == target) { cnt++; } else { cnt--; if (cnt == 0 ) { target = a[i]; cnt = 1 ; } } } return target; }
1.7 最小的K个数 part 快排思想
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 const int N = 105 ;int a[N] = {4 , 5 , 1 , 6 , 2 , 7 , 3 , 8 };int part (int *a, int left, int right) if (left < right) { int x = a[0 ], l = left, r = right; while (l < r) { while (l < r && a[r] >= x) r--; while (l < r && a[l] <= x) l++; if (l >= r) break ; swap (a[l], a[r]); } swap (x, a[l]); return l; } else return left; } void set_k (int *input, int n, int k) if (input == NULL || k > n || k <= 0 || n <= 0 ) { return ; } int start = 0 , end = n - 1 ; int index = part (input, start, end); while (index != k-1 ) { if (index > k-1 ) { end = index - 1 ; } else if (index < k - 1 ) { start = index + 1 ; } else { break ; } index = part (input, start, end); } }
1.8 数组中的逆序对 & 归并排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void mergeSort (int a[], int l, int r) if (l >= r) return ; int mid = (l+r) / 2 ; mergeSort (a, l, mid); mergeSort (a, mid+1 , r); int *arr = new int [r-l+1 ]; int k = 0 ; int i = l, j = mid + 1 ; while (i <= mid && j <= r) { if (a[i] <= a[j]) { arr[k++] = a[i++]; } else { arr[k++] = a[j++]; } } while (i <= mid) arr[k++] = a[i++]; while (j <= r) arr[k++] = a[j++]; for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) { a[i] = arr[i-l]; } delete []arr; }
1.15 约瑟夫环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import java.util.LinkedList;public class Solution public int LastRemaining_Solution (int n, int m) if (n < 1 || m < 1 ) return -1 ; LinkedList<Integer> link = new LinkedList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) link.add(i); int index = -1 ; while (link.size() > 1 ){ index = (index + m) % link.size(); link.remove(index); index --; } return link.get(0 ); } }
1.17 排序数组中某数字出现的次数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int bina (int *a, int len, int data) if (a == NULL || len <= 0 ) return -1 ; int l = 0 , r = len - 1 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = (l + r) / 2 ; if (a[mid] == data) return mid; else if (data < a[mid]) { r = mid - 1 ; } else l = mid+1 ; } return -1 ; }
linkedlist_summary
2.1 easy:
在 O(1) 时间删除链表节点, ✔️
删除单链表倒数第 n 个节点, ✔️
求单链表的中间节点, ✔️
判断单链表是否存在环, ✔️
从尾到头打印链表, 递归 ok., ✔️
链表中倒数第k个结点 ok., ✔️
判断两个无环单链表是否相交, ✔️
两个链表相交扩展:求两个无环单链表的第一个相交点, ✔️
两个链表的第一个公共结点 , ✔️
旋转单链表
题目描述:给定一个单链表,设计一个算法实现链表向右旋转 K 个位置。
环路的入口点
在第 4 题两个指针相遇后,让其中一个指针回到链表的头部,另一个指针在原地,同时往前每次走一步,当它们再次相遇时,就是在环路的入口点。
2.2 medium:
反转链表 next=head->next, head->next=pre, pre=head, head=next; 4步 ok, ✔️翻转部分单链表 举例:1->2->3->4->5->null, from = 2, to = 4 结果:1->4->3->2->5->null
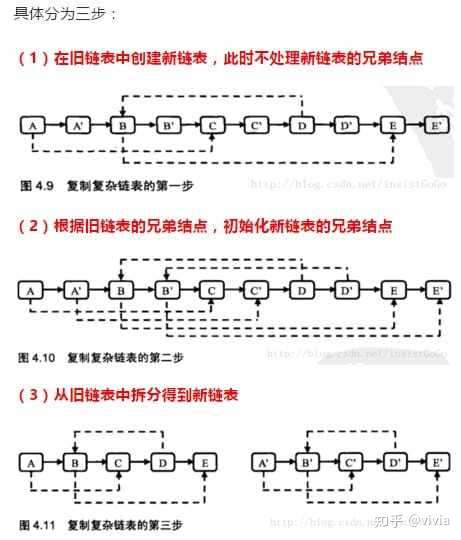
复杂链表的复制 ok, ✔️链表划分 (题目描述: 给定一个单链表和数值x,划分链表使得小于x的节点排在大于等于x的节点之前)
单链表排序
合并两个或k个有序链表 ok, 递归 (三元运算符).
删除链表重复结点 链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5. first->next=head, last, p 三针, ✔️
链表中环的入口结点, ✔️
单链表排序 or 合并两个或k个有序链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 struct Node {int value; }; Node* mergeList (Node* head1, Node* head2) { if (head1 == NULL ) return head2; if (head2 == NULL ) return head1; Node* tmp; if (head1->value < head2->value) { tmp = head1; head1 = head1->next; } else { tmp = head2; head2 = head2->next; } tmp->next = mergeList (head1, head2); return tmp; } Node* mergeSort (Node* head) { if (head == NULL ) return NULL ; Node* r_head = head; Node* head1 = head; Node* head2 = head; while (head2->next != NULL && head2->next->next != NULL ) { head1 = head1->next; head2 = head2->next->next; } if (head1->next == NULL ) return r_head; head2 = head1->next; head1 = head; r_head = mergeList (mergeSort (head1), mergeSort (head2)); return r_head; }
2.3 difficul:
链表求和
—
反转链表:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) ListNode next = null; ListNode pre = null while (head != null) { next = head.next; (保存当前头结点的下个节点) head.next = pre; (将当前头结点的下一个节点指向“上一个节点”,这一步是实现了反转) pre = head; (将当前头结点设置为“上一个节点”) head = next; (将保存的下一个节点设置为头结点) } return pre; }
复杂链表的复制:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Solution { public RandomListNode Clone (RandomListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null) return null; RandomListNode head = pHead; while (head != null){ RandomListNode node = new RandomListNode (head.label); node.next = head.next; head.next = node; head = node.next; } head = pHead; while (head != null){ head.next.random = head.random == null ? null : head.random.next; head = head.next.next; } head = pHead; RandomListNode chead = head.next; while (head != null){ RandomListNode node = head.next; head.next = node.next; node.next = node.next == null ? null : node.next.next; head = head.next; } return chead; } }
链表划分:
给定一个单链表和数值x,划分链表使得所有小于x的节点排在大于等于x的节点之前。
你应该保留两部分内链表节点原有的相对顺序。
样例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public ListNode partition (ListNode head, int x) if (head == null ) return null ; ListNode leftDummy = new ListNode(0 ); ListNode rightDummy = new ListNode(0 ); ListNode left = leftDummy, right = rightDummy; while (head != null ) { if (head.val < x) { left.next = head; left = head; } else { right.next = head; right = head; } head = head.next; } right.next = null ; left.next = rightDummy.next; return leftDummy.next; } }
13 道题搞定 BAT 面试——字符串
字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # include <iostream> # include <vector> # include <queue> # include <cstring> using namespace std;int main () string x; cin >> x; sort (x.begin (), x.end ()); reverse (x.begin (), x.end ()); cout << x << endl; return 0 ; }
3.1 easy:
替换空格, ✔️
反转字符串 abcd -> dcba, ✔️
翻转单词顺序列, I am a student. -> student. a am I, ✔️
旋转字符串, abcde --2位–> cdeab, 若干次旋转操作之后,A 能变成B,那么返回True, ✔️
左旋转字符串 string LeftRotateString(string str, int n),string Reverse(string str), ✔️
反转字串单词 string ReverseSentence(string str), reverse(str.begin(), str.end()); in lib algorithm
3.2 medium
字符流中第一个不重复的字符 (哈希来存每个字符及其出现的次数,另用一字符串 s 来保存字符流中字符顺序)第一个只出现一次的字符 字符串全排列 void res(char *str, char *pStr), scanf("%s", str); #include < utility>
字符串转整型 int StrToInt(char* str) ok
字符串的排列 (给定两个字符串 s1 和 s2,第一个字符串的排列之一是第二个字符串的子串)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.HashMap;public class Solution HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(); public void Insert (char ch) { s.append(ch); if (map.containsKey(ch)){ map.put(ch, map.get(ch)+1 ); }else { map.put(ch, 1 ); } } public char FirstAppearingOnce () { for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1 ) return s.charAt(i); } return '#' ; } }
3.2 difficult
KMP 算法
最长公共前缀
最长回文串 (3.1) 验证回文串 (3.2) 最长回文子串 (3.3) 最长回文子序列
表示数值的字符串
剑指offer: 表示数值的字符
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串”+100″,”5e2″,”-123″,”3.1416″和”-1E-16″都表示数值。 但是”12e”,”1a3.14″,”1.2.3″,”±5″和”12e+4.3″都不是。
3.1 easy code
3.1.1 替换空格
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 for (int i=tail; i>len && i>=0 ; i--){ if (str[len] == ' ' ) { str[i--] = '0' ; str[i--] = '2' ; str[i] = '%' ; } else { str[i] = str[len]; } len--; }
3.1.4 旋转字符串
1 2 3 4 5 class Solution public boolean rotateString (String A, String B) return A.length() == B.length() && (A+A).contains(B); } }
3.1.5 左旋转字符串
字符序列S=”abcXYZdef”,要求输出循环左移3位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。是不是很简单?OK,搞定它!
在第 n 个字符后面将切一刀,将字符串分为两部分,再重新并接起来即可。注意字符串长度为 0 的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Solution public String LeftRotateString (String str,int n) int len = str.length(); if (len == 0 ) return "" ; n = n % len; String s1 = str.substring(n, len); String s2 = str.substring(0 , n); return s1+s2; } }
3.2 medium code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void res (char *str, char *pStr) if (*pStr == '\0' ) cout << str << endl; for (char *p = pStr; *p != '\0' ; ++p) { char tmp = *p; *p = *pStr; *pStr = tmp; res (str, pStr+1 ); tmp = *p; *p = *pStr; *pStr = tmp; } }
字符流中第一个不重复的字符 C++
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 /class Solution { public : vector<char > vec; map<char , int > table; void Insert (char ch) { table[ch]++; vec.push_back (ch); } char FirstAppearingOnce () { for (char c : vec) { if (table[c] == 1 ) return c; } return '#' ; } };
字符流中第一个不重复的字符 Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import java.util.HashMap;public class Solution HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(); public void Insert (char ch) s.append(ch); if (map.containsKey(ch)){ map.put(ch, map.get(ch)+1 ); }else { map.put(ch, 1 ); } } public char FirstAppearingOnce () for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1 ) return s.charAt(i); } return '#' ; } }
4.1 easy
递归: 求二叉树中的节点个数 , ✔️
递归: 求二叉树的最大层数(最大深度) & (最小深度) 最小深度特殊情况:left || right==0 , ✔️
递归: 求二叉树第K层的节点个数 get_k(root.left, k-1) + get_k(root.right, k-1); good , ✔️
递归: 求二叉树第K层的叶子节点个数 if(k==1 and root.left and root.right is null) return 1; , ✔️
递归: 二叉树先序遍历/前序遍历 (fIno(Node* root) { while(1) {if else}
递归: 判断两棵二叉树是否结构相同 , ✔️
递归: 求二叉树的镜像(反转二叉树) , (左右递归交换)✔️
递归: 对称二叉树 (双函数,承接上题二叉树的镜像, good) , ✔️
递归: 求二叉树中两个节点的最低公共祖先节点 good , ✔️
递归: 求二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 good , ✔️
递归: 根据前序和中序重建二叉树 , ✔️
双函数,递归
树的子结构,遍历+判断, bool f5(Node* root1, Node* root2), bool son(Node* p1, Node* p2) , ✔️
判断二叉树是不是平衡二叉树 bool isBalance(Node* root), int maxHigh(Node* root) , ✔️
求二叉树的直径 (直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值), ✔️
4.2 medium
分层遍历 (判断二叉树是不是完全二叉树) (遍历到了NULL结点,如后续还有非NULL结点), ✔️
分层遍历 (自下而上分层遍历) bfs + vector< vector < int > >, ✔️
分层遍历 (按之字形顺序打印二叉树), ✔️
4.3 difficult:
二叉树中和为某一值的路径 void f4(Node* root, int exSum, int curSum, vecotr< int >& path), ✔️
二叉树下一结点:3情况 (1.有right.child 2.没有right.child,父left.child 3.没有right.child,父right.child)✔️序列化二叉树, String serialize(TreeNode root), TreeNode deserialize(String data) Queue queue = new LinkedList<>(); ✔️
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 bool f6(int* sec, int len), ✔️
二叉搜索树与双向链表 void convert(Node* root, Node*& pLast) , ✔️
二叉搜索树的第k个结点 , ✔️
二叉查找树节点的删除 . 重要
4.1 easy code
4.1.9 二叉树两节点的最低公共祖先
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 # include <iostream> # include <vector> # include <cstring> using namespace std;struct Node { Node* lchild; Node* rchild; int value; Node (): value (0 ), lchild (NULL ), rchild (NULL ) {} }; vector<Node*> vec1; vector<Node*> vec2; bool getNodePath (Node* root, Node* target, vector<Node*>& vec) if (root == NULl) { return false ; } vec.push_back (root); if (root == target) { return true ; } bool flag = false ; flag = getNodePath (root->lchild, target, vec) if (!flag && root->rchild) { flag = getNodePath (root->rchild, target, vec) } if (!flag) { vec.pop_back (); } return flag; } Node* getCom (const vector<Node*>& v1, const vector<Node*>& v2) { vector<Node*>::const_iterator it1 = v1.begin (); vector<Node*>::const_iterator it2 = v2.begin (); Node* pLast = NULL ; while (it1 != v1.end () && it2 != v2.end ()) { if (*it1 != *it2) { break ; } pLast = *it1; it1++; it2++; } return pLast; } int main () retunr 0 ; }
4.1.10 求二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Node* lowestCommonAncestor (Node* root, Node* p, Node* q) { if (root == NULL || p == NULL || q == NULL ) { return NULL ; } if (root->value > p->value && root > q->value) { return lowestCommonAncestor (root->lchild, p, q); } if (root->value < p->value && root < q->value) { return lowestCommonAncestor (root->rchild, p, q); } return root; }
4.1.11 前序中序重建二叉树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Node* f3 (int * pre, int * ino, int len) { if (pre == NULL || ino == NULL || len <= 0 ) return NULL ; int r_v = pre[0 ]; Node* root = new Node (); root->value = r_v; int i; for (i = 0 ; ; i++) { if (ino[i] == r_v) break ; } root->lchild = f3 (pre+1 , ino, i); root->rchild = f3 (pre+i+1 , ino+i+1 , len-1 -i); return root; }
双函数 + 递归
4.1.12 树2是否是树1的子结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 bool son (Node* p1, Node* p2) if (p2 == NULL ) { return true ; } if (p1 == NULL ) { return false ; } if (p1->value == p2->value) { return son (p1->lchild, p2-lchild); } } bool son_tree (Node* root1, Node* root2) if (root2 == NULL ) { return true ; } if (root1 == NULL ) { return false ; } if (root1->value == root2->child) { return son (root1, root2); } bool flag = false flag = son_tree (root1->lchild, root2); if (!flag) { return son_tree (root1->rchild, root2); } }
4.1.13 平衡二叉树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 bool isBalanced (Node* root) if (root == NULL ) return true ; return (-1 <= (maxHigh (root->lchild) - maxHigh (root->rchild)) <= 1 ) && isBalanced (root->lchild) && isBalanced (root->lchild); } int maxHigh (Node* root) if (root == NULL ) return 0 ; return max (maxHigh (root->lchild), maxHigh (root->rchild))+1 ; }
4.1.14 求二叉树的直径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private int diamHelper (TreeNode root) if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = diamHelper(root.left); int right = diamHelper(root.right); path = Math.max(path, left + right); return Math.max(left, right) + 1 ; }
4.2 medium code
4.2.1 判断二叉树是不是完全二叉树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 bool checkCompleteTree (Node* root) bool flag = true ; queue<Node*> q; if (root == null) return true ; q.push (root); while (!q.empty ()){ for (int i = 0 ; i < q.size (); ++i) { Node* tmp = q.front (); q.pop (); if (tmp->lchild == NULL && tmp->rchild != NULL ){ flag = false ; break ; } if (tmp->left != NULL ) que.push (tmp->left); if (tmp->right != NULL ) que.push (tmp->right); } } return flag; }
4.2.2 分层遍历 (自下而上分层遍历)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 vector<vector<int >> bfs (Node* root) { vector <vector<int > > ans; if (root == NULL ) return ans; queue<Node*> q; q.push (root); while (!q.empty ()) { vector<int > tv; for (int i = 0 ; i < q.size (); ++i) { Node* tmp = q.front (); q.pop (); if (tmp->lchild == NULL && tmp->rchild != NULL ){ flag = false ; break ; } if (tmp->left != NULL ) que.push (tmp->left); if (tmp->right != NULL ) que.push (tmp->right); tv.push_back (tmp->value); } ans.push_back (tv) } return flag; }
4.3 difficult code
4.3.1 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void f4 (Node*, int , int , vector<int >&) void f4 (Node* root, int exSum) if (root == NULL ) return ; vector<int > V; int curSum = 0 ; f4 (root, exSum, curSum, V); } void f4 (Node* root, int exSum, int curSum, vecotr<int >& path) curSum += root->value; path.push_back (root->value); if (curSum == exSum && root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL ) { } if (root->lchild) f4 (root->lchild, exSum, curSum, path); if (root->rchild) f4 (root->rchild, exSum, curSum, path); curSum -= root->value; path.pop_back (); }
4.3.3 序列化二叉树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public String serialize (TreeNode root) if (root == null ) return "#," ; StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(root.val + "," ); res.append(serialize(root.left)); res.append(serialize(root.right)); return res.toString(); } public TreeNode deserialize (String data) String [] d = data.split("," ); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < d.length; i++){ queue.offer(d[i]); } return pre(queue); } public TreeNode pre (Queue<String> queue) String val = queue.poll(); if (val.equals("#" )) return null ; TreeNode node = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val)); node.left = pre(queue); node.right = pre(queue); return node; }
4.3.4 二叉搜索树后序遍历的结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 bool f6 (int * sec, int len) if (sec == NULL ) return false ; if (len <= 1 ) return true ; int i, rv = sec[len-1 ]; for (i = 0 ; i < len-1 ; i++) { if (sec[i] > rv) break ; } for (int j = i; j < len-1 ; j++) { if (sec[j] < rv) return false ; } return f6 (sec, i) && f6 (sec+i, len-i-1 ); }
4.3.5 二叉搜索树与双向链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void convert (Node* root, Node*& pLast) if (root == NULL ) return ; if (root->lchild) convert (root->lchild, pLast); Node* pCur = root; pCur->lchild = pLast; if (pLast) pLast->rchild = pCur; pLast = pCur; if (root->rchild) convert (root->rchild, pLast); }
4.3.6 二叉搜索树的第k个结点
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。例如, (5,3,7,2,4,6,8)中,按结点数值大小顺序第三小结点的值为4。
因为二叉搜索树按照中序遍历的顺序打印出来就是排好序的,所以,我们按照中序遍历找到第k个结点就是题目所求的结点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int kthSmallest (TreeNode root, int k) if (root == null) return Integer.MIN_VALUE; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); int count = 0 ; TreeNode p = root; while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty ()){ if (p != null){ stack.push (p); p = p.left; }else { TreeNode node = stack.pop (); count ++; if (count == k) return node.val; p = node.right; } } return Integer.MIN_VALUE; } }
斐波拉契数列 & 跳台阶 & 变态跳台阶 2 * Fib(n-1). , ✔️
矩形覆盖 , ✔️
矩阵中的路径(BFS) 机器人的运动范围(DFS)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public int count (int threshold, int rows, int cols, int i, int j, int [][] flag) if (i<0 || j<0 || i>=rows || j>=cols || sum(i)+sum(j) > threshold || flag[i][j] == 1 ){ return 0 ; } flag[i][j] = 1 ; return 1 + count(threshold, rows, cols, i - 1 , j, flag) + count(threshold, rows, cols, i + 1 , j, flag) + count(threshold, rows, cols, i, j - 1 , flag) + count(threshold, rows, cols, i, j + 1 , flag); }
二进制中1的个数 n & n-1., ✔️
数值的整数次方 dp. , ✔️
数组中只出现一次的数字 ok. , ✔️
Stack & Queue
用两个栈实现队列包含min函数的栈栈的压入、弹出序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class MyQueue Stack<Integer> input = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> output = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push (int x) input.push(x); } public int pop () peek(); return output.pop(); } public int peek () if (output.isEmpty()){ while (!input.isEmpty()) output.push(input.pop()); } return output.peek(); } public boolean empty () return input.isEmpty() && output.isEmpty(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class MinStack Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> temp = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push (int x) stack.push(x); if (temp.isEmpty() || temp.peek() >= x) temp.push(x); } public void pop () int x = stack.pop(); int min = temp.peek(); if (x == min) temp.pop(); } public int top () return stack.peek(); } public int getMin () return temp.peek(); } }
栈的 push pop 序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Stack;public class Solution public boolean IsPopOrder (int [] pushA, int [] popA) if (pushA.length != popA.length || pushA.length == 0 || popA.length == 0 ) return false ; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < pushA.length; i++){ stack.push(pushA[i]); while (!stack.empty() && stack.peek() == popA[index]){ stack.pop(); index++; } } return stack.empty(); } }
最小的K个数 数据流中的第K大元素
滑动窗口最大值
前K个高频单词
爬楼梯 , ✔️
不同路径 II , ✔️
编辑距离 , ✔️
不同路径 II
如果当前没有障碍物,dp[m][n] = dp[m - 1][n] + dp[m][n - 1]
编辑距离
如果单词1第i+1个字符和单词2第j+1个字符相同,那么就不用操作,则DP[i + 1][j + 1] = DP[i][j];
如果不相同,则有三种可能操作,即增,删,替换。则取这三种操作的最优值,即dp[i + 1][j + 1] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i][j], Math.min(dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j]));
连续子数组的最大和 // dp: F[i] = max(a[i], F[i-1]+a[i]);
布尔数组
Longest Palindromic Substring/最长回文子串 给出一个字符串S,找到一个最长的连续回文串。
Interleaving String/交错字符串 输入三个字符串s1、s2和s3,判断第三个字符串s3是否由前两个字符串s1和s2交替而成且不改变s1和s2中各个字符原有的相对顺序。
数字数组
Unique Paths II/不同路径 (初始化很重要) , 起点到终点有多少条不同路径,向右或向下走。
Minimum Path Sum 矩阵左上角出发到右下角,只能向右或向下走,找出哪一条路径上的数字之和最小。Edit Distance/编辑距离 求两个字符串之间的最短编辑距离,即原来的字符串至少要经过多少次操作才能够变成目标字符串,操作包括删除一个字符、插入一个字符、更新一个字符。
Distinct Subsequences/不同子序列 给定S和T两个字符串,问把通过删除S中的某些字符,把S变为T有几种方法?
补充:京东2019实习编程题-删除0或部分字符使其成为回文串 见笔试整理总结
算法学习5
数据流中的中位数
滑动窗口的最大值 (双向队列)
正则表达式匹配 数值的整数次方 两个链表的第一个公共节点(2个stack or 长短链表相减)
diffcult
整数中1出现的次数 (判断每一位, 比如百位分别为 1, 0, 2~9, 后2种情况可合并)LRU Cache 需要深入学习Java的Map的内部实现
vector: vector::iterator, Modifiers (push_back, pop_back, insert)
array : len = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.LinkedList;public class Solution public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows (int [] num, int size) ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); LinkedList<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<Integer>(); if (num.length == 0 || size == 0 ) return res; for (int i = 0 ; i < num.length; i++){ if (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() <= i - size) deque.poll(); while (!deque.isEmpty() && num[deque.peekLast()] < num[i]) deque.removeLast(); deque.offerLast(i); if (i + 1 >= size) res.add(num[deque.peekFirst()]); } return res; } }
shopee
下一个更大元素 (Stack < Integer > (), Map < Int, Int > map, map.getOrDefault(nums1[i], -1); 序列为 9 2 1 4 借助栈实现,判断栈顶 和 下一个元素的大小 , ✔️鸡蛋掉落 (DP问题,难)google 扔鸡蛋,原题是 100 层楼,鸡蛋无限,答案 14 次。, ✔️
二叉树的右视图 (层次遍历) res.push_back(q.back()->val);, ✔️复杂链表指针 , ✔️
K 个一组翻转链表 1->2->3->4->5, 当 k = 2 时,应返: 2->1->4->3->5 , ✔️不同的二叉搜索树 , ✔️零钱兑换 完全背包问题 ,i=coins[j];i<=amount;,dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-coins[j]]+1); ✔️相交链表
有效的括号 (Stack来解决) , ✔️两数相加
[LeetCode] 887. Super Egg Drop 超级鸡蛋掉落 , ✔️
1 dp[i][j] = min (dp[i][j], max (dp[i - 1 ][k - 1 ], dp[i][j - k]) + 1 ) ( 1 <= k <= j )
之后可以再优化.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution : def isValid (self, s ): """ :type s: str :rtype: bool """ stack = list () match = {'{' :'}' , '[' :']' , '(' :')' } for i in s: if i == '{' or i == '(' or i == '[' : stack.append(i) else : if len (stack) == 0 : return False top = stack.pop() if match[top] != i: return False if len (stack) != 0 : return False return True
sina
两数之和 (链表 carry) , ✔️
最大子序和 , ✔️ 分治?
搜寻名人 (if (knows(res, i)) res = i;) , ✔️连续出现的数字 , ✔️
搜索二维矩阵 , ✔️
排序链表
翻转二叉树 , ✔️
买卖股票的最佳时机 系列
字符串转整型
无重复字符的最长子串 , ✔️ (借助hashmap)
Tencent
Minimum Factorization 最小因数分解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public : ListNode* addTwoNumbers (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { int carry = 0 ; ListNode* fakeHead = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode* curr = fakeHead; while (l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL | carry != 0 ) { if (l1 != NULL ) { carry += l1->val; l1 = l1->next; } if (l2 != NULL ) { carry += l2->val; l2 = l2->next; } ListNode* node = new ListNode (carry % 10 ); carry /= 10 ; curr->next = node; curr = node; } return fakeHead->next; } };
m_15 二叉树非递归的 先根遍历和中序遍历 (必会数据结构之一)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 void fPre (Node* root) Node* p = root; stack<Node*> S; while (1 ) { if (p != NULL ) { cout << p->value << ' ' ; S.push (p); p = p->lchild; } else { if (S.empty ()) return ; p = S.top (); S.pop (); p = p->rchild; } } } void fIno (Node* root) Node* p = root; stack<Node*> S; while (1 ) { if (p != NULL ) { S.push (p); p = p->lchild; } else { if (S.empty ()) return ; p = S.top (); S.pop (); cout << p->value << ' ' ; p = p->rchild; } } }









Checking if Disqus is accessible...