
1. Flow Chart Explanation
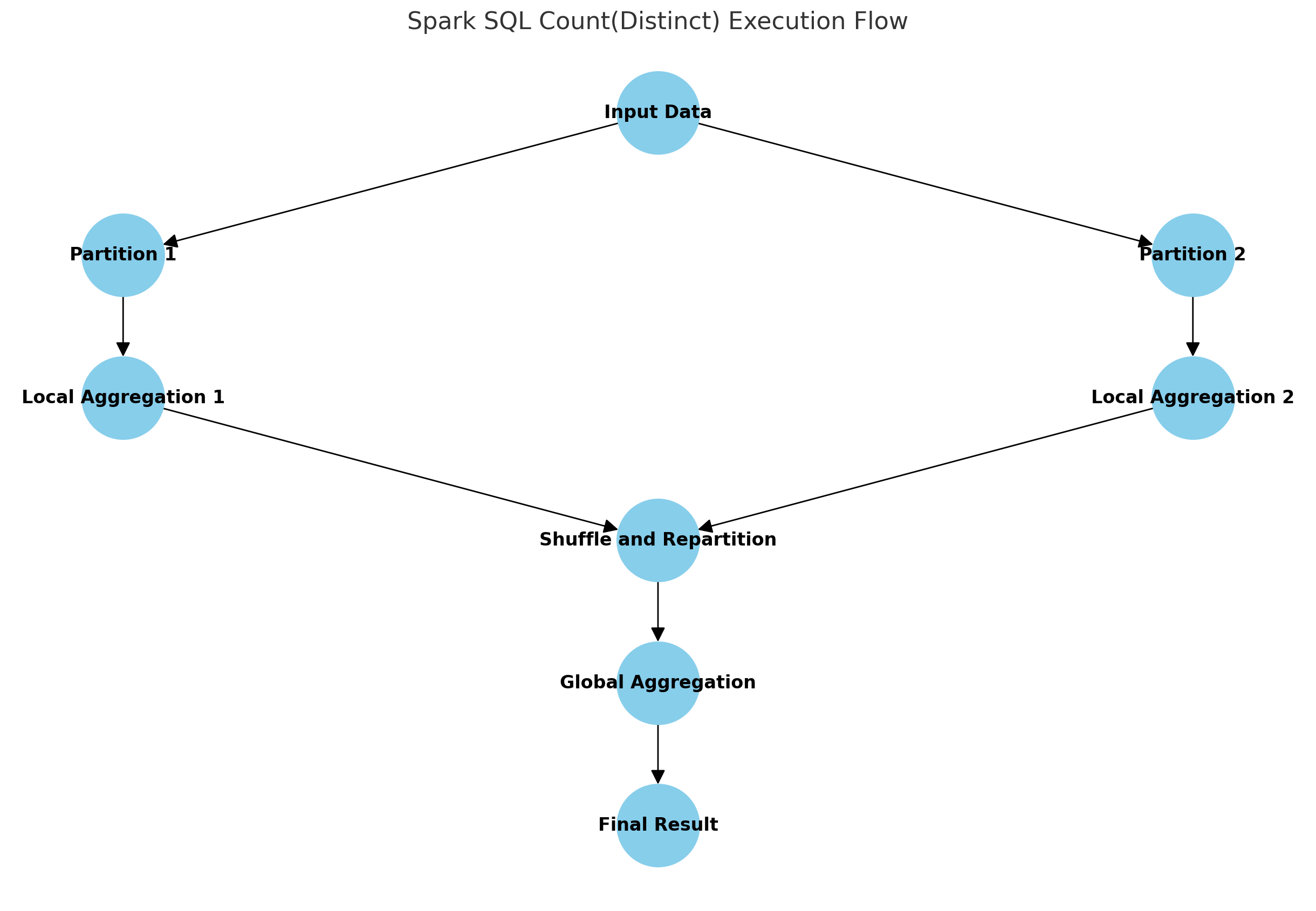
-
Input Data:
- Data is read and partitioned.
- 数据被读取并分区。
-
Partition Processing (Partition 1 and Partition 2):
- Data is assigned to different partitions for processing.
- 数据被分配到不同的分区进行处理。
-
Local Aggregation (Local Aggregation 1 and Local Aggregation 2):
- Local deduplication and aggregation are performed within each partition, reducing the amount of data to be transmitted.
- 在每个分区内,先进行局部去重和聚合,减少需要传输的数据量。
-
Shuffle and Repartition:
- The local aggregation results are repartitioned through a shuffle operation to ensure that data with the same key is sent to the same partition.
- 将局部聚合结果通过 Shuffle 操作重新分区,确保相同键的数据被发送到同一个分区。
-
Global Aggregation:
- Global deduplication and aggregation are performed within the repartitioned partitions to calculate the final deduplication result.
- 在重新分区后的分区内进行全局去重和聚合,计算最终的去重结果。
-
Final Result:
- The final
count(distinct)result is obtained. - 得到
count(distinct)的最终结果。
- The final
2. Example Data
Assume the data in table table_a is as follows:
假设 table_a 表的数据如下:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 3 | Alice |
| 4 | Carol |
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 5 | Dave |
| 6 | Eve |
3. Query
1 | SELECT |
expand 操作是 SparkSQL 用来处理多个 count(distinct) 聚合时的一种常见优化策略。特别是在查询中有多个 count(distinct) 的情况下,SparkSQL 可能会使用 expand 操作来将数据扩展到多个副本,这样每个副本可以独立地计算一个 count(distinct)。
在 count(distinct) 中的作用:
如果你有多个 count(distinct) 操作,例如 count(distinct id) 和 count(distinct name),SparkSQL 可能会使用 expand 操作将数据集扩展为两个(或多个)副本,这样 id 和 name 可以在各自的副本中单独计算。
expand 操作的结果是数据量会增加(数据膨胀),但这允许 SparkSQL 更好地并行计算多个 count(distinct) 操作。
4. Internal Optimization
4.1: Partial Aggregation
Local count(distinct) operations are performed within each partition first, reducing the amount of data to be transmitted.
在每个分区内部先进行局部 count(distinct) 操作,减少需要传输的数据量。
Partition 1:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 3 | Alice |
| 4 | Carol |
Local aggregation results:
局部聚合结果:
id:[1, 2, 3, 4]name:[Alice, Bob, Carol]
Partition 2:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 5 | Dave |
| 6 | Eve |
Local aggregation results:
局部聚合结果:
id:[1, 2, 5, 6]name:[Alice, Bob, Dave, Eve]
4.2: Shuffle Operation
The local aggregation results are repartitioned through a shuffle operation.
将局部聚合结果通过 Shuffle 操作重新分区。
Partitions after Shuffle:
-
Partition 1:
id:[1, 2, 3, 4]id:[1, 2, 5, 6]
-
Partition 2:
name:[Alice, Bob, Carol]name:[Alice, Bob, Dave, Eve]
4.3: Global Aggregation
Global aggregation is performed within the repartitioned partitions.
在重新分区后的分区内进行全局聚合。
Global Aggregation Results 全局聚合结果:
count(distinct id)= 6count(distinct name)= 5
Through this process, Spark SQL effectively reduces the amount of data transmission and computation, fully utilizing distributed computing resources, thereby optimizing the performance of the count(distinct) operation.
通过这种方式,Spark SQL 有效地减少了数据传输量和计算量,充分利用分布式计算资源,从而优化了 count(distinct) 操作的性能。






Checking if Disqus is accessible...